Background on blood pressure
Healthcare providers assess blood pressure using a blood pressure monitor, or sphygmomanometer. This tool produces a reading based on two types of blood pressure: systolic and diastolic.
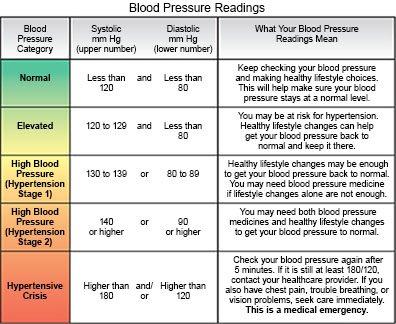
Systolic pressure refers to the pressure inside blood vessels as the heart forces blood out to the rest of the organs. Diastolic pressure refers to the pressure inside blood vessels as the heart rests between beats. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
A sphygmomanometer displays the systolic pressure reading above the diastolic pressure reading. If a person has a normal blood pressure, for example, the monitor will display a systolic pressure of less than 120 mm Hg over a diastolic pressure of less than 80 mm Hg.
